Last Updated on October 29, 2023
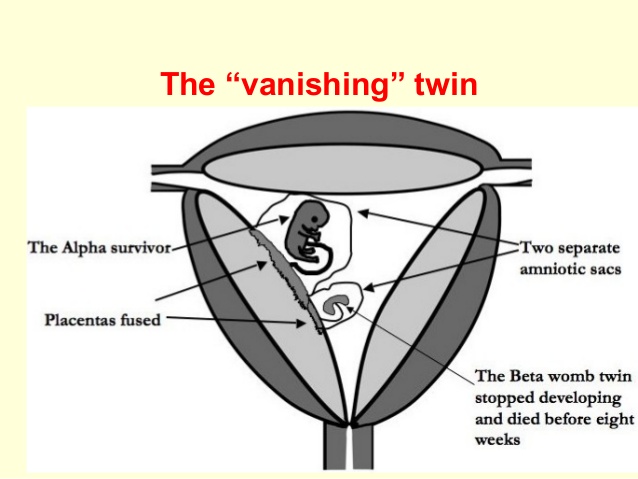
Image Credit
Vanishing twin syndrome is said to occur when there is a multifetal gestation with subsequent disappearance of one or more fetuses.
For vanishing twin syndrome to occur
- There are twins or multiples in the uterus during pregnancy
- Twin or multiples dies as result of a miscarriage.
- The fetal tissue of dead fetus is absorbed by the other twin, multiple, placenta or the mother giving appearance of a vanishing twin.
Vanishing twin syndrome wasfirst described by Stoeckel in 1945.
The resorption of the fetus may be complete or there is a formation of fetus papyraceus (ie, a “mummified” or compressed fetus).
The placenta may develop a cyst, subchorionic fibrin, or amorphous material.
Vanishing twin syndrome occurs in 21-30% of multifetal gestation.
Cause and Pathophysiology of Vanishing Twin Syndrome
Exact cause of vanishing twin syndrome is unknown but following factors are suggested to play role.
- Fetalr chromosomal abnormalities [in the vanished twin]
- Improper cord implantation
- Advanced maternal age
If the event occurs in first trimester, the mother may develop mild vaginal bleeding and cramping.
In late first trimester, second trimester and third trimester, there is danger of premature labor, infection from a retained fetus, puerperal hemorrhage and consumptive coagulopathy.
Obstruction of labor due to low-lying fetus papyraceus may occur.
Increases both preterm (< 37 weeks) and very preterm (< 32 weeks) births is noted
The surviving fetus has an increased risk of cerebral palsy if the event occurs in the second half of pregnancy.
Aplasia cutis or areas of skin necrosis may also occur. This occurs in twins connected through vascular connection due to temporary hypotension in the surviving twin at the time of death of other fetus.
There is also increase risk of congenital anomalies like microcephaly or hydrocephaly.
Clinical Presentation
Usually the presentation occurs during the first trimester of pregnancy. The most common presenting complaints include bleeding, uterine cramps, and pelvic pain.
Vaginal bleeding may be observed on pelvic examination.
Differential Diagnoses
- Threatened abortion
- Subchorionic hemorrhage
Lab Studies
- Increase in pregnancy associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and free beta-hCG has been reported.
- Alpha-fetoprotein levels are elevated than a normal twin pregnancy.
- Serial beta-human chorionic gonadotropin shows lesser than expected rate of increase.
The biochemical markers are of little values in presence of dead fetus visible on ultrasound. These are useful if gestational sac is empty.
Imaging
Ultrasonography is used to confirm the diagnosis of early twin pregnancy. Follow-up ultrasonography reveals the pregnancy loss (vanishing twin).
Treatment
Uncomplicated vanishing twin syndrome requires no special medical care.
In fetus papyraceus, the pregnancy is monitored for premature labor, obstruction of labor, or death of the surviving fetus due to placental abruption or chorioamnionitis.
Instruct pregnant women to seek medical care for vaginal bleeding, cramping, and pelvic pain.
This fetus is also at risk for low birth weight and small for gestational age with increasing risk in the surviving twin for vanishing twin occurring later in gestation
The viable twin should receive specialized medical care as indicated by initial physical examination and subsequent mental and physical development.
Dilation and curettage may be done if both fetuses die.
