Last Updated on October 29, 2023
Heart rate is the number of times that our heart contracts or beats in a minute. The main function of the heart is to maintain adequate blood supply [Heart sends oxygenated blood to the body so that tissues could extract the oxygen for their use]. Therefore the rate varies according to the demands of the body.
The normal rate of the heart at rest for healthy adults, including older-aged adults and kids >10 years is between 60 and 100 heartbeats a minute.
Resting heart rate is the rate at which our heart beats when we are resting or relaxed.
When we say normal, we mostly refer to resting heart rate.
With exertion, our heart rate goes up as the demand for oxygen increases. The heart, by upping the rate of beating [and pumping blood] tries to meet the increased demand. Along with this, the breath rate also increases because lungs function more to extract more oxygen from the inhaled air.
Anxiety, fear, surprise also lead to an increase in the heart rate. This is caused by the release of adrenaline or epinephrine in the body, preparing us for fight or flight.
The normal heart rate undergoes healthy variation, going up in response to some conditions, including exercise, body temperature, body position (such as for a short while after standing up quickly), and emotion (such as anxiety and arousal).
Heart rate and Pulse
Pulse is defined as the number of times arteries expand and contract in response to the heartbeat.
This rate is exactly equal to the heartbeat, the rate of heart contractions because these heart contractions cause an increase in blood pressure as well as pulse rate in the arteries.
Pulse, therefore, is a direct measure of heart rate.
Except in some conditions where the heart may beat faster than the pulse shows.
The pulse volume may be affected by changes in the arteries. An absence of pulse may indicate a problem in the vessel.
How to Take Pulse?
You must have taken or seen people taking [doctor, nurses, paramedicals or actors in the movies] pulse from neck or wrist.
A pulse is taken at the point where arteries run closely under the skin. Wrist and neck are common points where pulses are taken but there are other places in the body where you could take the pulse.
The wrist is the most common place to take the pulse. It measures the pulse
The easiest way to monitor your heart rate is to take your pulse at the wrist.
Resting Normal Heart Rate
The normal resting heart rate for healthy adults, including older-aged adults and kids>10 years is between 60 and 100 heartbeats a minute.
Sportspersons and athletes who train themselves vigorously can have a heart rate as low as 40 beats per minute
Variation with age
A newborn’s heart beats very fast and reaches the average at 10 years of age. Here is the rough guide of normal heart rate at different times of life.
| Newborn to 1st month | 70-190 |
| 1-11 months | 80-110 |
| 1-2 years | 80-130 |
| 3-4 years | 80-120 |
| 5-6 years | 75-115 |
| 7-9 years | 70-110 |
| >10 years | 60-100 |
- Tachycardia means the heart is beating too fast at rest (usually over 100 beats a minute)
- Bradycardia is a heart rate that is too slow (usually below 60 beats a minute).
Effect of Exercise on Heart
During exercise, the rate goes up due to increased oxygen demand. But regular athletic exercise lowers both the resting heart rate and the maximum rate during exertion.
Thus resting rate of athletes who are training regularly is lower than that of less active people.
Similarly, the person who is regularly trained would have a lower rate at the peak of exercise as compared to an untrained one.
This happens due to increased vagal tone in response to exercise.
According to the American Heart Association, the maximum heart rate during exercise roughly equals 220 minus age.
So a typical 35-year-old’s maximum rate during exercise is around 185 beats a minute.
For best effects without any adverse effect on the heart, the target should be to reach between 50-85% of the maximum heart rate for a given age. This is called target heart rate.
How does the heart keep beating?
The heart has a natural pacemaker called sinoatrial or SA node which is made of cells capable of generating current. These cells generate electrical impulse which via a special circuit is transmitted to atria and ventricles [different chambers of heart] so that they beat in a rhythmical fashion.
Electrical functioning of the heart is checked by a commonly known procedure, electrocardiogram or ECG.
How to Check Heart Rate
Heart rate is an indicator of heart’s function. So its examination is an important clinical parameter. There are different methods to check.
Pulse
Pulse is an indirect measure of the rate and other functions of the heart. The pulse is felt when an artery can be palpated close to skin against some underlying bone.
A pulse can tell us about pulse rate, pulse volume, and regularity of the beats]
How to check Pulse at the Wrist?
- Hold one of your hands out with the palm facing upwards and the elbow slightly bent.
- Place your index (first) and middle fingers of your other hand on the inside of your wrist, just below the base of your thumb
- Press the two fingers lightly on your skin until you feel your pulse. This pulse is of radial artery.
- If you feel nothing, either press harder or search with your fingers for the artery and press again.
You can count the number of beats for a full 60 seconds. Or count till 30 seconds and multiply by 2. Some count till 20 seconds or even 15 and multiply accordingly.
By any method, the normal rate is the value obtained for 60 seconds.
Alternatively, the pulse can be found by pressing the two fingers on the side of your neck (carotid artery). This is just beside Adam’s apple in the hollow area.
Other places where you can check the pulse
- The popliteal artery – This is an extension of the femoral artery and can be palpated behind the knee. It is a deep artery and can be palpated with some difficulty.
- The abdominal aorta – It lies over the abdomen. It is difficult to palpate in an obese person.
- The basilar artery – It is close to the ear behind the pinna.
- The brachial artery – It is present just above the elbow under the biceps.
- The dorsalis pedis – It lies in the middle of dorsum of the foot in proximity to the base of the first metacarpal.
- The femoral artery – It lies in the groin.
- The posterior tibial artery – It is present at the ankle joint just behind the medial malleolus.
- The superficial temporal artery – It lies at the temple, about two fingerbreadths from the anterosuperior margin of the pinna.
Using a Monitor
Monitors or pulsometers, allow you to measure your heart rate in real time. Some of them even record data for later study.
These are popular among athletes and people who exercise regularly.
There are two popular types :
Chest Strap and Watch
It consists of two parts. You place the watch around your wrist and a strap around your chest.
Strapless Heart Rate Monitor
The device is wrapped around the wrist, part of the back of your hand, and your index finger.
A pulse represents the arterial palpation of the heartbeat by placing fingertips at the places where an artery could be felt by pressing it against the near-surface.
The radial pulse is commonly measured. Other sites are
- Neck – carotid artery
- Wrist- radial artery
- Groin – Femoral artery
- Knee-popliteal artery
- Ankle – posterior tibial artery
- Foot – dorsalis pedis artery
The pulse was first described by Claudius Galen.
Characteristics of Normal pulse
A pulse is generated because of the pressure waves caused by the pumping action of the heart.
It is the indirect measure of heartbeat and activity of the heart. The normal pulse has a small anacrotic wave on the upstroke which is not felt. This is followed by a big tidal or percussion wave which is felt by the palpating finger.
On the following downstroke, there is a notch followed by a wave both of which are not normally palpable.
The following are the characteristics that are looked for when palpating-
- Rate
- beats per minute a
- The rate varies in resting state and activity as the physiological demands vary.
- Mostly, the pulse rate and heart rate are equal but in case of premature beats or atrial fibrillations, the heart rate may be more than the pulse rate
- The difference is called the pulse-rate deficit.
- In adults, the normal pulse appears at regular intervals and has a rate between 60-100 per min. There may be a mild variation in the rate between the two phases of respiration which is called sinus arrhythmia.
- Rhythm
- regular which interval between two beats is always equal.
- An irregular rhythm might indicate sinus arrhythmia.
- [Other causes of irregularity – ectopic beats, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia, atrial flutter, partial heart block, etc.]
Force
- Pulse force or volume is the force or strength of the pulse felt when palpating.
The force provides an idea of how hard the heart has to work to pump blood out of the heart and through the circulatory system.
The force is recorded using a scale
- 3+ Full, bounding
- 2+ Normal/strong
- 1+ Weak, diminished, thready
- 0 Absent/non-palpable
A 1+ force may reflect a decreased stroke volume [ can be seen in heart failure, heat exhaustion, or hemorrhagic shock, etc.]
A 3+ force may reflect an increased stroke volume and is seen with exercise, stress, fluid overload, and high blood pressure.
- Pulse Equality
A comparison with the opposite side
In coarctation of aorta or supravalvular aortic stenosis, femoral pulse may be significantly delayed as compared to radial. This is an important finding and aids in diagnosis.
Different Types of Abnormal Pulses
The normal pattern may become abnormal in different conditions. Abnormal pulses indicate a variation in heart activity. Here is a list of different types of pulses in the body.
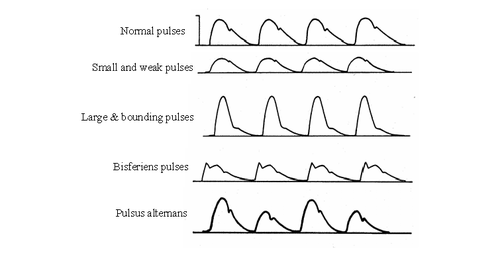
- Anacrotic
- slow-rising, twice-beating pulse w
- best felt in the carotid artery in aortic stenosis.
- Pulsus Bisferiens
- rapidly rising, twice-beating pulse:
- Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis
- Severe Aortic Insufficiency with mild Aortic Stenosis
- Pulsus Parvus ET Tardus
- slow rising pulse like the anacrotic pulse but the anacrotic wave is not felt. It is seen in aortic stenosis.
- Pulsus Alternans
- strong and weak beat occurring alternately, probably due to alternate rather than regular contraction of the muscle fibers of the left ventricle.
Causes are left ventricular failure, toxic myocarditis, paroxysmal tachycardias. It may occur for several beats following a premature beat.
- Pulsus paradoxus
Systolic blood pressure normally the drop is more than 10 mmHg on inspiration
can cause disappearanc of pulse on inspiration
superior vena cava obstruction, lung conditions like asthma, emphysema or airway obstruction, cardiac conditions like pericardial effusion, constrictive pericarditis and severe congestive cardiac failure.
- Pulsus Bigeminus
Pulsus bigeminus is the coupling of the waves in a pair, followed by a pause. It is seen in alternate premature beats, A.V. block, and sinoatrial block with ventricular escape.
- Thready Pulse
The pulse rate is rapid and the pulse wave is small and disappears quickly. This is seen in shock especially cardiogenic.
- Waterhammer Pulse
Large bounding pulse
It may be seen in fever, alcohol consumption and pregnancy. It is also seen in high output states like anemia, beriberi or cor pulmonale, cirrhosis, Paget’s disease, AV fistula, thyrotoxicosis, etc.
Cardiac lesions like aortic regurgitation, rupture of sinus of Valsalva into the heart chambers, patent ductus arteriosus, aortopulmonary window, and systolic hypertension may show Waterhammer pulse as well.

