Last Updated on October 29, 2023
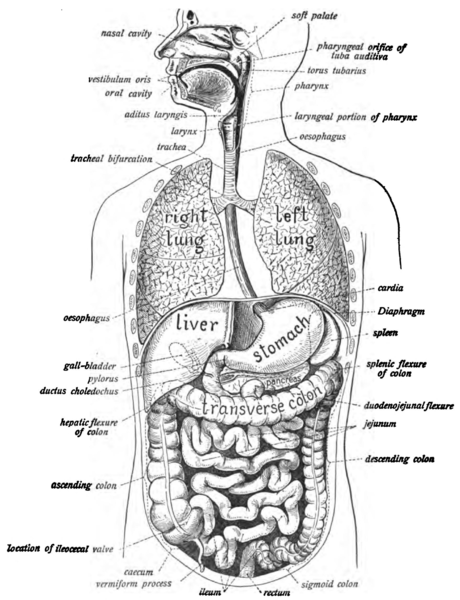
Gastrointestinal diseases are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract or digestive system tract is a system of serially connected organs from the mouth to the anus.
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus are major regions of the digestive system.
Symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases are of various types. These symptoms can occur in isolation or together.
Careful analysis of the clues provided both from the gut itself and from the effect of gut disease on the body as a whole is required if a diagnosis is to be made.
There are some symptoms that occur during normal gut functioning and cannot be considered as symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases.
For example, thirst and hunger are common symptoms. Hunger may be associated with epigastric discomfort or pain when intense.
Thirst can cause a sensation of dryness of the mouth.
As we eat food, the swallowing is normally perceived, and there is temperature sensation in the upper and mid-esophagus, as well as in the mouth. Normal gastric motility can, to some extent, be perceived and so could the movement of gas and fluid in the gut, called borborygmi.
The sensation of rectum and colon prior to defecation felt as a call to stool, or during constipation is part of routine physiology and aspects of the normal sensation of gut activity.
But various diseases can cause these routine perceptions to alter and new symptoms may appear.
Various Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Diseases
Eructation or Belching
Eructation or belching [also known as burping, ructus, or eructation] is the release of gas from the digestive tract (mainly esophagus and stomach) through the mouth.
It is usually accompanied with a typical sound and, at times, an odor.
Belching is typically caused by expelling the air swallowed when eating or drinking.
The sound of burping is caused by the vibration of the upper esophageal sphincter as the gas passes through it.
Belching is normally associated with regurgitation especially in lying position.
The valve at the top of the stomach does not produce a tight seal, and in the absence of gravity, the stomach contents may come up along with the expelled air.
Causes of Eructation
- Drinking carbonated drinks such as beer, soft drinks, energy drinks
- Common diabetes drugs like metformin
- Hiatus hernia
- Food allergy
- Ulcer, acid reflux disease, H. pylori, and gastritis
- Gall bladder problems like cholecystitis
- Mouth breathing
- Psychogenic causes like anxiety or depression
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. It is the sensation of something sticking in the throat or chest during swallowing. It indicates a problem in the esophagus. Dysphagia could indicate esophageal stricture, from benign or malignant causes.
It is a potentially serious symptom that should always be investigated. It is a pointer to some underlying disease.
Causes of dysphagia
- Esophagitis – an inflammation in the esophagus
- Esophageal webs- thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and submucosa
- Esophageal strictures
- Esophageal tumors
- Achalasia cardia- failure of relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter
- Esophageal spasm
- Hiatus hernia
- Chagas’ disease (American trypanosomiasis)
- Scleroderma
- Radiation
- Pharyngeal & laryngeal Lesions
- External compression
- Cervical spondylitis
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Goiter
- Enlarged left atrium
- Aneurysm
- Neurological
- Bulbar palsy
- Polyneuropathy
- Motor neuron disease
- Myopathies
- Myasthenia
- Dermatomyositis.
Painful swallowing
This symptom is different from dysphagia and should not be confused with it. Here, there is a pain on swallowing but the difficulty or sticking sensation is absent. It is usually due to local infection. It can occur in pharyngitis. It also occurs in patients with AIDS in whom candida or herpes simplex often occur in the esophagus.
Heartburn
Heartburn is the burning sensation due to acid reflux from the stomach into the lower part of the esophagus. It causes pain in the epigastrium, chest, and neck. It is difficult to distinguish from angina pectoris. Heartburn occurs usually at night when the patient lies flat in the bed, or after bending or stooping when abdominal pressure is increased.
Causes of heartburn
- Reflux esophagitis
- Hiatus hernia
- Peptic ulcer
- Faulty dietary habits
- Addictions
- Neurosis
Dyspepsia or Indigestion
This is actually a group of symptoms that include heartburn, pain, distension, nausea or ‘an acid feeling’ occurring after eating or drinking. The patients may also use this term to describe an inability to digest food. The symptom is subjective, frequent, and usually benign in origin. It sometimes may be associated with peptic ulcers.
Cause of indigestion
- Upper gastrointestinal tract
- Alcohol
- Heavy meals
- Aerophagia
- Hiatus hernia
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Gastritis
- Drugs
- Lower gastrointestinal tract
- Parasites
- Food intolerance
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Increased intraluminal gas
- Hepatobiliary
- Cholecystitis
- Stones
- Pancreatitis
- Splenic flexure syndrome
- Systemic diseases
- Uremia
- Cardiac failure
- Tuberculosis
- Malignancy
- Functional
Flatulence
It describes excessive wind. It is associated with belching, abdominal distension, and the passage of flatus per rectum. It usually represents a functional disturbance in which excessive air is swallowed. Certain foods produce relatively large amounts of gas, for example, legumes, resulting in increased flatulence. Very infrequently flatulence is associated with organic disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
Common causes of flatulence
- Gastric Causes:
- Aerophagy
- Neurosis
- Hiatus hernia
- Pyloric stenosis
- Biliary dyspepsia
- Following vagotomy
- Food intake
- Cabbage
- Cauliflower
- Peas
- Beans
- Intestinal
- Steatorrhea
- Intestinal obstruction
- Malignancy, etc.
- Systemic diseases
- Cardiac failure
- Cirrhosis
Hiccups
Hiccups are commonly occurring benign repeated sudden diaphragmatic contraction, often triggered by upper gastrointestinal irritation. They go on their own. Occasionally hiccups indicate brainstem disease.
Nausea and Vomiting
Everyone once in a while has experienced both nausea and vomiting. Some people feel them more as compared to others. Vomiting is a neurogenic response triggered by chemoreceptors in the brainstem or reflexly through irritation of the stomach. Vomiting consists of a phase of nausea, followed by hypersalivation, pallor, sweating, and hyperventilation.
Retching is the term used for an involuntary effort to vomit which may or may not be followed by the expulsion of gastric content through nausea and vomiting.
Causes of nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal Causes
- Gastritis ulcer
- Peptic ulcer
- Colics
- Acute abdominal emergencies
- Appendicitis
- Cholecystitis
- Peritonitis
- Pancreatitis
- Intestinal obstruction
- Cardiac:
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiac failure
- Central
- Raised intracranial tension
- Meningitis
- Meniere’s disease
- Motion sickness
- Radiation
- Metabolic
- Diabetes
- Alcohol intake
- Pregnancy
- Hypercalcemia
- Addison’s disease
- Toxic
- Febrile illnesses
- Viral hepatitis
- Drugs
- Corrosive poisons
- Functional
Read more about Nausea-Causes, Investigations, Home Remedies and Treatment
Constipation
Constipation is a subjective complaint. The patient gets a sense of inadequate emptying of the bowel by defecation. The term is sometimes used to describe the passage of hard stools, irrespective of stool frequency.
Constipation is most commonly used to indicate a decrease in the frequency of stools. The frequency of stool varies from person to person. The passage of formed stool with a frequency of twice a week is usually taken to indicate an abnormality of bowel frequency in clinical practice.
Causes of constipation
Acute Constipation
- Intestinal obstruction
- Volvulus-abnormal twisting of the intestine causing obstruction
- Intussusception- infolding of one part of the intestine into another
- Incarcerated hernia
- Acute abdomen
- Appendicitis
- Salpingitis- inflammation of fallopian tubes
- Perforation of gut
- Colic or pain abdomen
Chronic Constipation
Constipation that is slow to develop and is present for a long time.
- Faulty habits
- Laxative abuse
- Prolonged travel
- Insufficient dietary roughage
- Painful anal conditions
- Piles
- Fissures
- Organic obstruction
- Carcinoma
- Diverticulum
- Strictures
- Adynamic bowel
- Scleroderma
- Myopathies
- Myotonia
- Metabolic
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypokalemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Porphyria
- Lead poisoning
- Drugs
- Atropine and related drugs
- Opium group
- Tricyclic antidepressants
Diarrhea
Diarrhea consists of watery stools of large volume which may or may not contain blood. It indicates frequent loose motions. Usually, diarrhea occurs due to viral or bacterial infection.
Chronic diarrhea should raise the possibility of malabsorption with steatorrhoea. Steatorrhoea is the passage of pale, bulky stools containing excessive fats that commonly float in water and are difficult to flush away.
Causes of diarrhea
- Osmotic causes
- Laxative abuse
- Maldigestion of food
- Infections
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Amebiasis
- Giardiasis
- Helminthiasis
- Endocrine diseases
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Diabetes
- Addison’s disease
- Drugs
- Thyroxine
- Prostigmin
- Ampicillin
- Phenolphthalein
- Anxiety
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Miscellaneous
- Malignant carcinoid syndrome
Abdominal Pain
Depending upon the causation, the pain may occur in the upper abdomen, in the hypochondrium, in the lower abdomen, or in the rectum. The important features of abdominal pain are its site, intensity, the character of duration, and frequency. Aggravating and relieving factors should be noted.

Pain abdomen is a very common complaint and symptom of many underlying diseases.
Causes of abdominal pain
- Acid peptic disease
- Peritonitis
- Paralytic ileus
- Mechanical obstruction of hollow viscus
- Colic
- Intestinal
- Renal
- Biliary
- Vascular disturbances causing ischemia
- Thromboembolism
- Sickle cell crisis
- Rupture of an aneurysm
- Abdominal wall causes
- Hernia through linea alba
- Trauma
- Infection
- Referred pain
- Pneumonia
- Pleurisy
- Ischemic heart disease
- Panniculitis
- Torsion of the testes or ovary
- Metabolic
- Diabetes
- Uremia
- Porphyria
- Lead poisoning
- Neurogenic
- Herpes zoster
- Tabes dorsalis
- Functional
Abdominal Distension
Abdominal distension has many causes. It may relate to flatulence, or more commonly to functional bowel disease in which the viscera are enlarged because their contractility is diminished from the disease of the bowel musculature, or its innervation. Distension is also a feature of steatorrhoea [passage of fat-laden stool], or from visceral enlargement in liver disease.
Weight Loss
Malabsorption of food, loss of appetite, or starvation are common causes of weight loss. It is also a feature of malignancy.
Hematemesis
Hematemesis is the passage of blood in vomiting. It results from bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Rectal Bleeding
It results from bleeding in the rectum or anal canal, most commonly from piles but sometimes from anal or rectal carcinoma. Hematochezia is the term used for the passage of fresh blood through the anus. It indicates a pathology in the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Melena refers to the passage of dark, partially digested blood along feces. It implies bleeding from a site more proximal than the rectum, usually in the upper colon or small intestine.
Jaundice refers to the yellowish appearance of skin and conjunctiva of eyes. It may be associated with other cutaneous systemic features of liver disease, often along with dark urine. Jaundice is caused by increased bilirubin levels and implies a disease of the liver or the biliary tract.
Jaundice could also result from excessive hemolysis.
These symptoms cover most of the gastrointestinal disease presentation.
