Last Updated on August 2, 2019
Digital clubbing or nail clubbing or finger clubbing is bulbous enlargement of soft parts of the terminal phalanges with both transverse and longitudinal curving of the nails. The swelling of the terminal phalanges in clubbing occurs due to interstitial edema and dilation of the arterioles and capillaries.
Digital clubbing is also called fingernail clubbing or nail clubbing. Drumstick fingers and watch-glass nails are other names for these deformed nails.
Though clubbed fingers are mostly asymptomatic, these may predict the presence of some dreaded underlying diseases. Clubbing of nails results in an increase in both anteroposterior and lateral diameter of the nails. Clubbing was first described by Hippocrates nearly 2500 years ago in a patient with empyema and is regarded to be the oldest sign in clinical medicine.
Digital clubbing may occur as an isolated finding or is often part of the syndrome of hypertrophic osteoarthropathy.
Grades of Clubbing
- Fluctuation and softening of the nail bed (increased ballotability)
- Loss of the normal <165° angle (Lovibond angle) between the nailbed and the fold (cuticula)
- Increased convexity of the nail fold
- Thickening of the whole distal (end part of the) finger (resembling a drumstick)
- Shiny or glossy changes in a nail with striation of the nail and skin
The process usually takes years but in certain conditions like lung abscess and empyema of the thorax, clubbing may develop quite fast.
Grading of clubbing has no clinical significance.
Causes of Digital Clubbing
Many conditions from different organ systems may produce digital clubbing. These are
Pulmonary Diseases
- Bronchogenic carcinoma
- Lung abscess
- Bronchiectasis
- Tuberculosis with secondary infection
- Diffuse fibrosing alveolitis
Cardiac Diseases
- Infective endocarditis
- Cyanotic heart disease
- Congenital heart disease
Gastrointestinal Diseases
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Cholangiolitic cirrhosis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Endocrine Diseases
- Iatrogenic myxedema
- Exophthalmos
- Acromegaly
Miscellaneous Causes
- Hereditary
- Idiopathic
- Unilateral- Pancoast tumor, subclavian and innominate artery aneurysm
- Unidigital- Traumatic or gout deposit
- In heroin addicts due to chronic obstructive phlebitis [inflammation of vein]
Different Types of Clubbing
Unilateral Clubbing
Clubbing is generally bilateral, but in some conditions, it may occur unilaterally. Unilateral clubbing is usually associated with local vascular lesions of the arm, axilla, and thoracic outlet and with hemiplegia.
Aneurysm of the subclavian artery is commonly reported in the literature to cause unilateral clubbing. An aortic aneurysm and innominate artery aneurysm have also been reported.
Unilateral clubbing also occurs in arm affected by hemiplegia. The pathogenesis of clubbing in hemiplegia is not clear.
Clubbing may also involve single digit only in case of digital mucoid cyst, osteoid osteoma, myxochondroma, and enchondromas.
Differential Clubbing
Occasionally, clubbing may occur in lower limbs, sparing the upper limbs. This is known as differential clubbing. Differential clubbing may occur in a patient with patent ductus arteriosus associated with pulmonary artery hypertension and right to left shunt.
Congenital
Congenital nail clubbing is known to occur and is usually symmetrical and bilateral, but different fingers and toes may be involved to varying degrees. Some fingers or toes may be spared, but the thumbs are almost always involved.
Pseudoclubbing
In hyperparathyroidism, excessive bone resorption may result in the disappearance of the terminal phalanges with telescoping of soft tissues and a drumstick appearance of the finger resembling clubbing. However, the curvature of the nail is not present.
Assessment of Clubbing
Clubbing can be assessed by physical examination. However, it is subjective and often unreliable, particularly in mild cases. Computerized analysis has been used to objectively assess clubbing.
Different signs of clubbing are:
Lovibond’s Angle
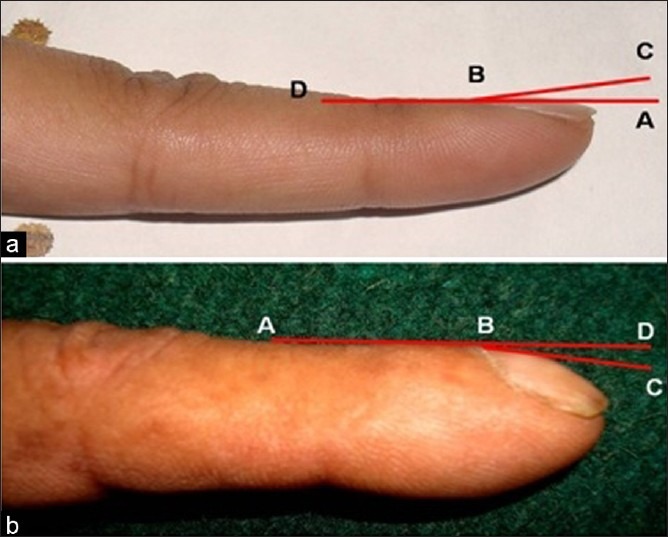
It was proposed by Lovibond and is also called Profile angle. It is defined by the angle made by the nail as it exists from the proximal nail fold. In normal subjects, the profile angle is usually less than 165 degrees. Profile angle of greater than 180° can be used to differentiate true clubbing from simple nail curving and paronychia.
Hyponychial angle
It is constructed by drawing a line from the distal digital crease to the cuticle and another line from the cuticle to hyponychium [see above]. Normal hyponychial angle is less than 192°. Hyponychial angle is a preferred objective criterion for clubbing because it is independent of age, sex, height, and weight of the patient and correlates with the subjective assessment of clubbing.
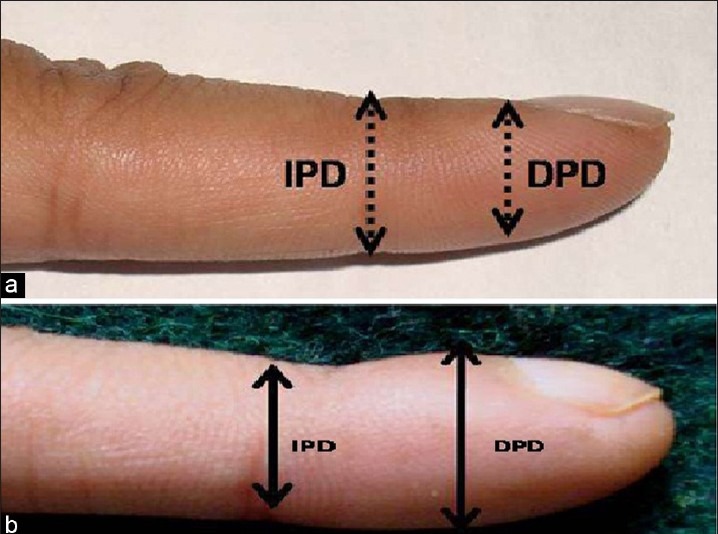
Phalangeal Depth Ratio
It is the ratio of the digit’s depth measured at the junction between skin and nail (nail bed) and at the distal interphalangeal joint. Normally, the depth at the distal interphalangeal joint is more than the depth at nail bed but in clubbed fingernails, connective tissue deposition expands the pulp in the terminal phalanx and the ratio becomes reversed. This ratio is also independent of age, sex, and ethnicity of the population.
A Phalangeal depth ratio of over 1 is indicative of clubbing.
Digital Index
It is the sum of the phalangeal depth ratio for all 10 fingers. A digital index of 10.2 or higher is indicative of clubbing. Digital index is more specific for clubbing than phalangeal depth ratio.
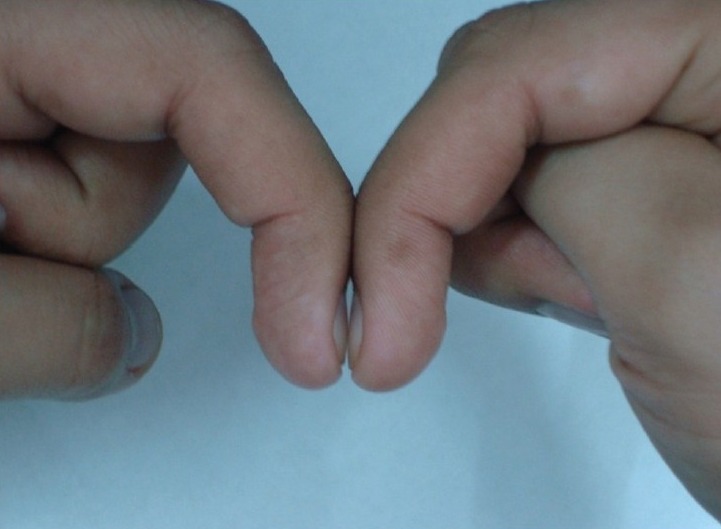
Schamroth’s Test or Schamroth’s Window Test
This test was originally demonstrated by South African cardiologist Dr. Leo Schamroth on himself and is a popular test for clubbing.
When the distal phalanges (bones nearest the fingertips) of corresponding fingers of opposite hands are directly apposed (placed against each other back to back), a small diamond-shaped “window” is normally apparent between the nailbeds.
If this window is obliterated, the test is positive and clubbing is present. Though popular, this test is not very accurate.
Precision and accuracy of this sign are not known.
Significance of Digital Clubbing
Clubbing is a clinical sign which may indicate and prompt the workup for an underlying disease. It is often seen in pulmonary conditions.
However, clubbing is also seen in some people without any underlying disease.
There is no treatment required for clubbing
References
Image Credit: Sarkar M, Mahesh DM, Madabhavi I. Digital clubbing. Lung India : Official Organ of Indian Chest Society 2012;29(4):354-362. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.102824. Article