Last Updated on August 18, 2023
Bethesda system is a system for reporting cervical and vaginal cytology or Pap smear results.
It was developed during a workshop sponsored by the National Cancer Institute at Bethesda, Maryland in the United States. It was first introduced in 1988 and later revised in 1991 and 2001.
The primary objective of this system was to introduce a standardized protocol that would enable consistent and precise communication of pap smear findings between laboratories, clinicians and patients.
The terminology used in this system also reflects the currently understood biological concepts underlying cervical neoplasm and pre-cancerous lesions.
The pre-cancerous lesions were earlier referred to as cervical dysplasia (mild, moderate or severe) or cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN 1, CIN 2 or CIN 3).
This variable usage by clinicians and laboratories had resulted in great confusion. So in the Bethesda system, these terms were discarded and instead, an easily reproducible and understood, two-tiered approach was adopted-low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) and high-grade squamous intra-epithelial lesion (HSIL).
Most of the laboratories are currently using the Bethesda system for reporting of cervical smears.
Specimen Type
Indicate if the sample is
- conventional smear
- liquid-based preparation
- other
Specimen Adequacy
- Satisfactory for evaluation (describe the presence or absence of endocervical/transformation zone component and other quality indicators e.g., partially obscuring blood, inflammation, etc)
- Unsatisfactory for evaluation …(specify reason)
- Specimen rejected/not processed (specify reason)
- A specimen processed and examined but unsatisfactory for evaluation of epithelial abnormality because of …(specify reason)
General Categorisation (Optional)
- Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy
- Other: See interpretation/ result ( eg. Endometrial cells in a woman >= 45 years of age)
- Epithelial cell abnormality: See interpretation/ result (specify ‘squamous’ or ‘glandular’ as appropriate)
Interpretation / Result
Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy
(When there is no cellular evidence of neoplasia, state this in the general categorization above and/ or in the Interpretation/ Result section of the report-whether or not there are organisms or other non-neoplastic findings)
Nonneoplastic findings (optional to report)
- Nonneoplastic cellular variations
- Squamous metaplasia
- Keratotic changes
- Tubal metaplasia
- Atrophy
- Pregnancy-associated changes
- Reactive cellular changes associated with
- Inflammation (includes typical repair)
- Lymphocytic (follicular) cervicitis
- Radiation
- Intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD)
- Glandular cells status post hysterectomy
Organisms
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Fungal organisms morphologically consistent with Candida spp
- Shift in flora suggestive of bacterial vaginosis
- Bacteria morphologically consistent with Actinomyces spp
- Cellular changes consistent with Herpes simplex virus
- Cellular changes consistent with cytomegalovirus
Other
Endometrial cells (in a woman >= 45 years of age)
(specify if “negative for squamous intra epithelial lesion”)
Epithelial Cell Abnormalities
Squamous cell
- Atypical squamous cells
- of undetermined significance (ASC-US)
- cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
- Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
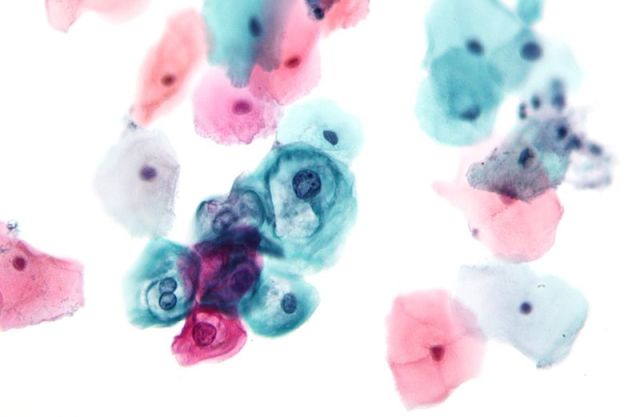
LSIL in Bethesda system Pap Stain
(Encompassing: HPV/ mild dysplasia/ CIN1)
- High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)
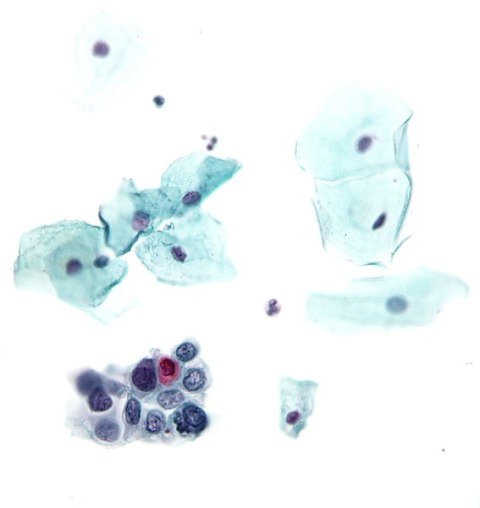
(Encompassing: moderate and severe dysplasia, CIS, CIN2, CIN 3)
- With features suspicious for invasion( if invasion is suspected)
- Squamous cell carcinoma

Glandular cell
- Atypical
- Endocervical cells (NOS or specify in comments)
- Endometrial cells (NOS or specify in comments)
- Glandular Cells (NOS or specify in comments)
- Atypical
- Endocervical cells favour neoplastic
- Glandular cells favour neoplastic
- Endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ
- Adenocarcinoma
- Endocervical
- Endometrial
- Extrauterine
- Not otherwise specified(NOS)
Other malignant neoplasms: (specify)
Adjunctive testing
Provide a brief description of the test method(s) and report the result so that it is easily understood by the clinician.
Computer Assisted Interpretation Of Cervical Cytology
If case reported by an automated device, specify device and result.
Educational Notes And Comments Appended To Cytology Reports (Optional)
Suggestions should be concise and consistent with clinical follow-up guidelines published by professional organizations (references to relevant publications may be included)
